
It’s important to understand how this method works, especially if you’re studying accounting or managing finances. We will cover everything from the basics to examples, making it easy for anyone to grasp. Hence, our calculation of the depreciation expense in Year 5 – the final year of our fixed asset’s useful life – differs from the prior periods. The double declining balance method accelerates this by using twice the straight-line depreciation rate, allowing for larger deductions in the early years of an asset’s life. Depreciation is an accounting process by which a company allocates an asset’s cost throughout its useful life. Firms depreciate assets on their financial statements and for tax purposes in order to better match an asset’s productivity in use to its costs of operation over time.
Example 2: Depreciation of Machinery with Variable Lifespan

To calculate it, you take the asset’s starting value, find its useful life, and then multiply the starting value by double the double declining balance method straight-line rate. By mastering these adjustments, I can better manage my assets and their depreciation, ensuring that my financial statements reflect the true value of my investments. There are four different depreciation methods used today, and I discuss these in the last section of my Beginner’s Guide to Depreciation.

Example of DDB Depreciation
This accelerated depreciation approach can reduce taxable income more significantly in the initial years, offering potential tax benefits. Additionally, the DDB method does not subtract the residual value at the beginning, unlike the straight-line method. Firstly, it results in higher depreciation expenses in the early years of an asset’s life, which reduces taxable income and, consequently, taxes owed during those years.

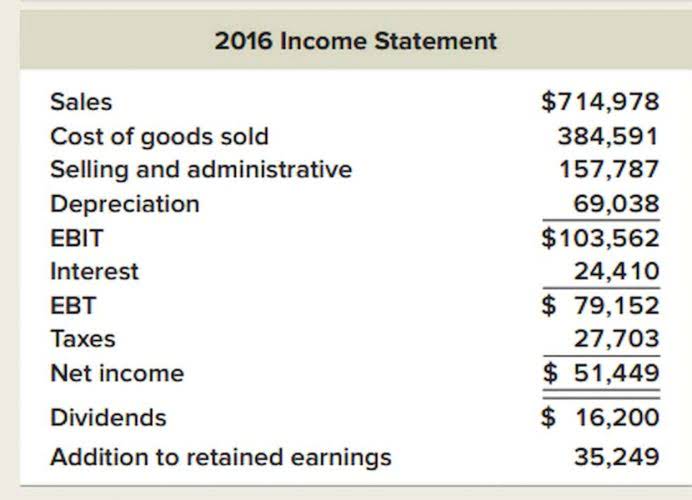
Analyze the Income Statement
The carrying value of an asset decreases more quickly in its earlier years under the straight line depreciation compared to the double-declining method. In the last year of an asset’s useful life, we make the asset’s net book value equal to its salvage or residual value. This is to ensure that we do not depreciate an asset below the amount we can recover by selling it. It is important to note that we apply the depreciation rate on the full cost rather than the depreciable cost (cost minus salvage value). For example, if an asset has a useful life of 10 years (i.e., Straight-line rate of 10%), the depreciation rate of 20% would be charged on its carrying value. Under straight line depreciation, XYZ Company would recognize $3,000 in depreciation expense each year.
What is Double-declining Balance Depreciation?
- So, in the first year, the company would record a depreciation expense of $4,000.
- In the last year, ignore the formula and take the amount of depreciation needed to have an ending Net Book Value equal to the Salvage Value.
- We should have an Ending Net Book Value equal to the Salvage Value of $2,000.
- The Double Declining Balance Method, often referred to as the DDB method, is a commonly used accounting technique to calculate the depreciation of an asset.
- Additionally, any changes must be disclosed in the financial statements to maintain transparency and comparability.
It was first enacted and authorized under the Internal Revenue Code in 1954, and it was a major change from existing policy. The Double-Declining Balance (DDB) depreciation method is a robust tool in the accounting and financial sectors, particularly for assets with rapid initial value depreciation. Understanding its application and benefits ensures more accurate financial reporting and strategic tax planning. By accelerating depreciation in the earlier years, DDB aligns expenses with the actual utility derived from the asset, providing a clearer financial picture. The declining balance method is one of two accelerated depreciation methods, and it uses a depreciation rate that unearned revenue is a multiple of the straight-line method rate.
Double Declining Depreciation
Depreciation in the year of disposal if the asset is sold before its final year of useful life is therefore equal to Carrying Value × Depreciation% × Time Factor. This pattern continues until the book value approaches the salvage value, ensuring depreciation never exceeds the asset’s worth. Yes, businesses can switch methods if they find another one suits their needs better. At the end of the second year, we subtract the first year’s depreciation from the asset’s cost, and then apply 40% to that number. This formula is called double-declining balance because the percentage used is double that of Straight-line. With doola Bookkeeping, small business owners get powerful, founder-friendly tools that simplify every part of accounting.
Example 3: Double-Declining Depreciation in Last Period
Don’t worry—these formulas are a lot easier to understand with a step-by-step example. Recovery period, or the useful life of the asset, is the period over which you’re depreciating it, in years. Get free guides, articles, tools and calculators to help you navigate the financial side of your business with ease.

How to calculate accumulated depreciation
- Each method serves a distinct purpose based on the asset’s usage pattern, making it crucial for businesses to choose the most appropriate approach to match the asset’s life cycle and performance.
- By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the depreciation expense for each year of the asset’s useful life under the double declining balance method.
- Various depreciation methods are available to businesses, each with its own advantages and drawbacks.
- It turns the initial cost of the asset into an ongoing expense, spread across the asset’s useful life, giving you a more accurate financial picture.
- The net book value is calculated by deducting the accumulated depreciation from the cost of the fixed asset.
A double-declining balance depreciation method is an accelerated depreciation method that can be used to depreciate the asset’s value over the useful life. It is a bit more complex than the straight-line method of depreciation but is useful for deferring tax payments and maintaining low profitability in the early years. Some companies use accelerated depreciation methods Debt to Asset Ratio to defer their tax obligations into future years.
Accelerating the computer equipment’s depreciation with the double declining balance method reduces your taxable income at a time when every dollar is precious. You could use it to extend cash runway or scale your fledgling operation, such as by hiring top talent, acquiring initial customers or developing your product. In business and tax accounting, it’s how you deduct the cost of your assets over time—but there’s more than one way to do it. The double declining balance method is one option, and it can be invaluable when you want to maximize your deductions upfront. Additionally, the company may provide further detail on its depreciation methods and assumptions in the notes to the financial statements. This may include information on the useful lives and salvage values used for each asset and the depreciation rates and methods applied.
- The double declining balance method is a method used to depreciate the value of an asset over time.
- The double declining balance depreciation method shifts a company’s tax liability to later years when the bulk of the depreciation has been written off.
- Per Publication 946, the IRS requires most businesses to use the General Depreciation System (GDS) version of the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) to calculate depreciation for tax purposes.
- At the end of their 10-year useful life, it is expected that the fixtures will be worthless.
- Under the DDB method, higher depreciation expense is taken in the early years to match it with the higher revenue the asset generated.
Understanding GAAP requirements for depreciation in financial statements and reports. Manufacturing equipment and assets where usage patterns decline over time but not as dramatically as technology assets. Accountingo.org aims to provide the best accounting and finance education for students, professionals, teachers, and business owners. If the double-declining depreciation rate is 40%, the straight-line rate of depreciation shall be its half, i.e., 20%. Double-declining depreciation charges lesser depreciation in the later years of an asset’s life. Therefore, it is more suited to depreciating assets with a higher degree of wear and tear, usage, or loss of value earlier in their lives.